Tag Overview
<html>, <body>, <head>, <title>
<html>Represents the root (top-level element) of an HTML document, so it is also referred to as the root element
All other elements must be descendants of this element.
<body>- Everything inside the body tag is shown inside the browser window
<head>Contains information about the page (vs shown on the pages
Title and Links to other files are usually specified in the head element
<title>- Text here is displayed in the top of the browser (or on the tab in Chrome or other browsers that use tabs)
<title> is just one of many tags that can be placed inside of <head>, we’ll see more of them as we go through the class, for more information click here
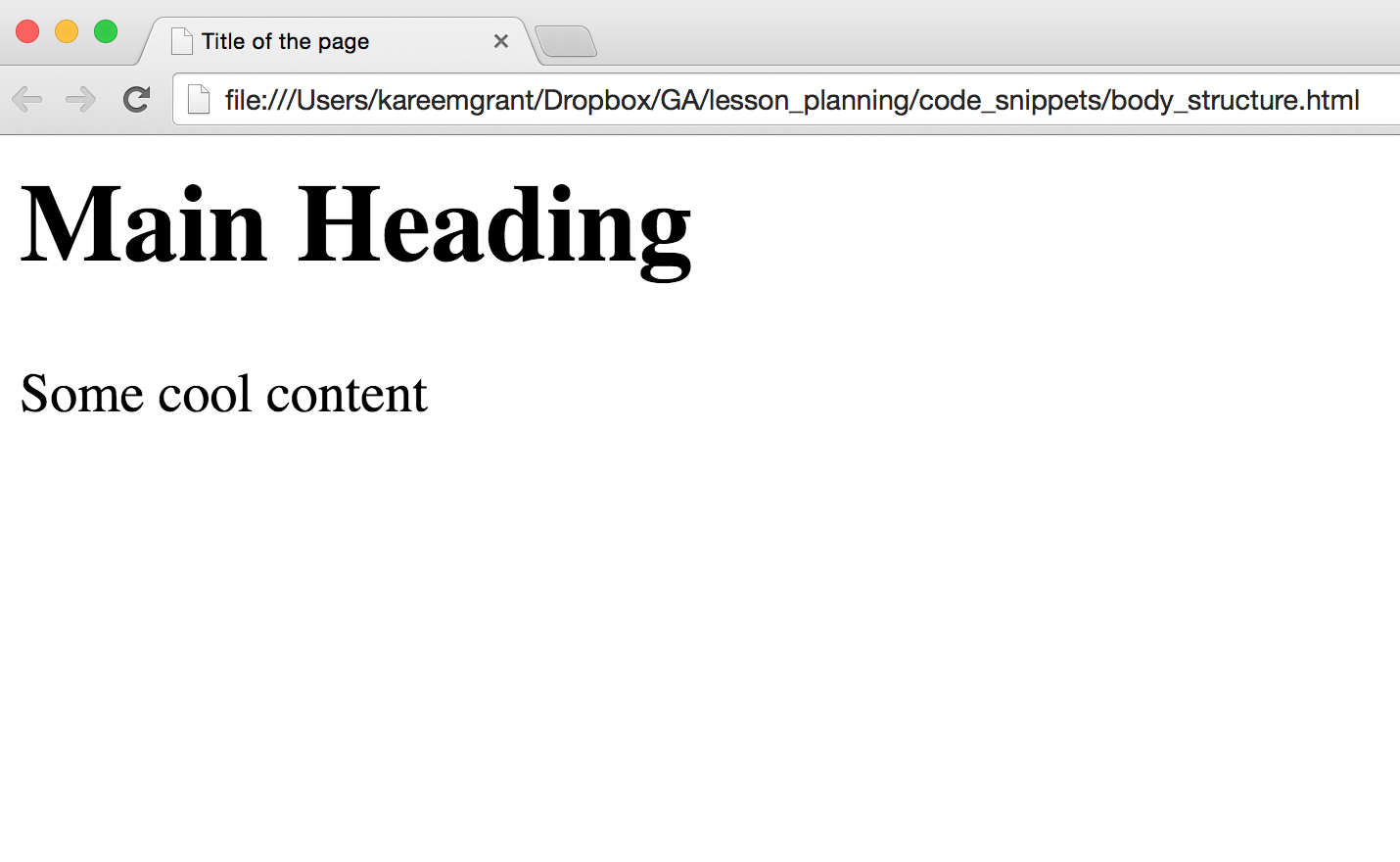
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- contains information about the page -->
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Main Heading</h1>
<p>Some cool content</p>
</body>
</html>
HTML Headings
- Six (6) levels of headings
- h1 tags is used for main headings
- h2 tags are used for subheadings
- Remaining level headings used as needed based on your content hierarchy
Browsers display headings differently, but relative sizes will always be consistent (by default) - i.e. h1 will always be bigger than h2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- contains information about the page -->
<title>My page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Main Heading</h1>
<h2>level 2 heading</h2>
<h3>level 3 heading</h3>
<h4>level 4 heading</h4>
<h5>level 5 heading</h5>
<h6>level 6 heading</h6>
</body>
</html>

Paragraphs
Use
<p>element to display paragraphsBy default, browser displays each paragraph on a new line
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- contains information about the page -->
<title>My page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is a paragraph. Become familiar with it because you will be using it a lot.</p>
<p>Content inside of a paragraph is displayed on separate lines</p>
<p> The browser will view this line of text as separate from the other two paragraphs above, despite how it looks in the text editor</p>
</body>
</html>

Lists
- 3 different types of lists:
- Unordered - lists start with a bullet point by default
- Ordered - numbered lists
- Definition - set of terms along with definition of those terms (not used often)
Example of unordered list
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- contains information about the page -->
<title>My page</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>one</li>
<li>two</li>
<li>three</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>

List items elements are the items within list, they use opening and closing tag
list item elements are indented by default
list items elements are always a child a list element (in this case the “unordered list” or ul element.
Links
Links created using the
<a>taglink tags use the href attribute (remember attributes come with a name and a value)
The value of the href attribute is the location where the link will direct you after it has been clicked
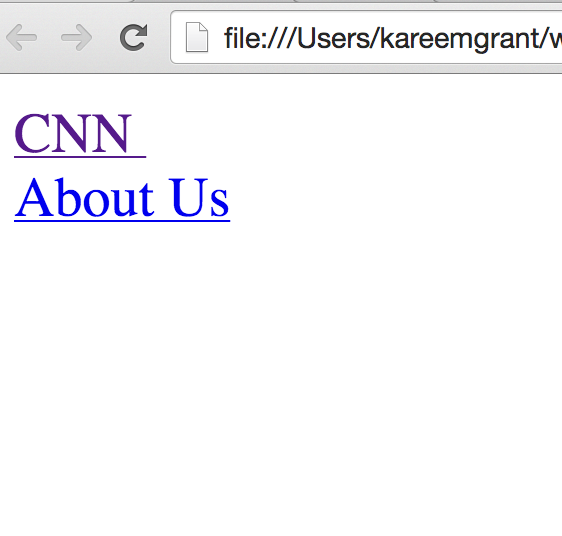
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- contains information about the page -->
<title>My page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.cnn.com"> CNN </a>
<a href="/about_us.html">About Us</a>
</body>
</html>
Images
Images are placed in a
<img>Empty element meaning there is no closing tag
<img src="images/team_hands" alt="a group of people touching hands in a star formation" title="teamwork is awesome">
Image Attributes
src - Tells browser where to find the image (may relative or absolute path)
alt - Provides description of image for people who cannot see the image (accessibility)
title - Used to provide additional information about the image. Most browsers will display this information in a tooltip.
Image File Formats
.png - Supports transparency and semi-transparency, great for logos, icons, and repeating background tiles. Almost always preferable to a gif.
.gif - Can have basic transparency, typically a png is used instead
.jpeg - No transparency, can be stored at different compression levels with varying amounts of “lossy-ness”, typically the best format for photos
Many more tags
<b> Makes text bold</b>
<i> Italic text </i>
<br/> Used to break text within a paragraph
<hr /> Used to add a horizontal line to visually break up text
MDN (Mozilla Developer Network) is an excellent resource for all things HTML, CSS and Javascript. For a complete list of all tags avaiable click here