Last Class Review
Topics We Covered Last Class
Block, Inline and Inline-Block elements
Containing elements:
<div>and semantic tagsCSS Floats
Block, Inline and Inline-Block elements
Block Level Elements
By default, block elements take up an entire row regardless of the width of their content
Example block elements:
<p>,<h1>,<div>Full list of block level elements can be found here
Inline Elements
Sit within a block level element and do not start on a new line
By default, inline elements only occupy the horizontal space needed to fit its content
The height and width properties of an inline element will not be recognized
Example inline elements:
<a>,<img>,<span>Full list of inline elements can be found here
Inline-Block
Allows you make an element inline while also allowing the element to recognize height and width properties
inline-block is set as a value of the display property in CSS
Containing elements
Elements that contain groups of elements
For example, grouping all of the elements associated with the header in a
<div><div>tags are commonly used as containing elements

In example the above example, orange lines represent <div> tags
<div>
Used to group a set of elements together in one block-level box
<div>element are block-level elements which means they will start on a new line
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Sample Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<!-- start of header div -->
<div id="header">
<img src="images/logo.gif" alt="Anish Kapoor" />
<ul>
<li><a href="index.html">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="biography.html">Biography</a></li> <li><a href="works.html">Works</a></li>
<li><a href="contact.html">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<!-- end of header div -->
</body>
</html>
Structure using <div>s
Prior to HTML5, the divs have been the most common way to structure content on page
Usual ids/classes are used to provide each div with context regarding the type of content div contains
Above picture is just an example! This structure is not set in stone, use what makes sense for your project
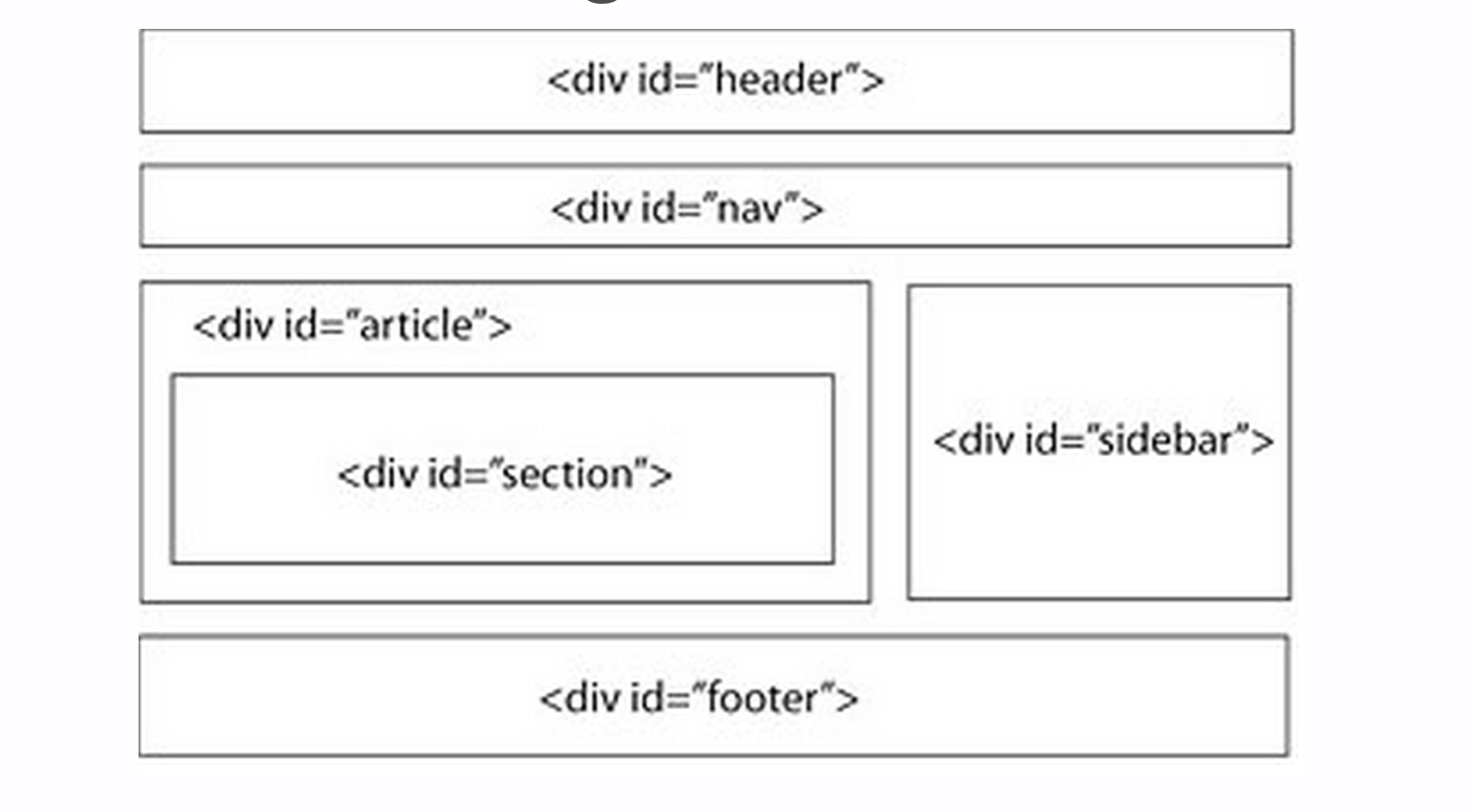
<div>s are used to structure pages in logical sections/groups based on your site’s layout
Structure using Semantic tags
Similar to
<div>s, semantic tags are container elementsHTML5 introduced semantic tags that directly communicate type of content the container element contains
Important note: incorrect use of the tags will not result in any errors (but may be confusing for your teammates)
Above picture is just an example! This structure is not set in stone, use what makes sense for your project
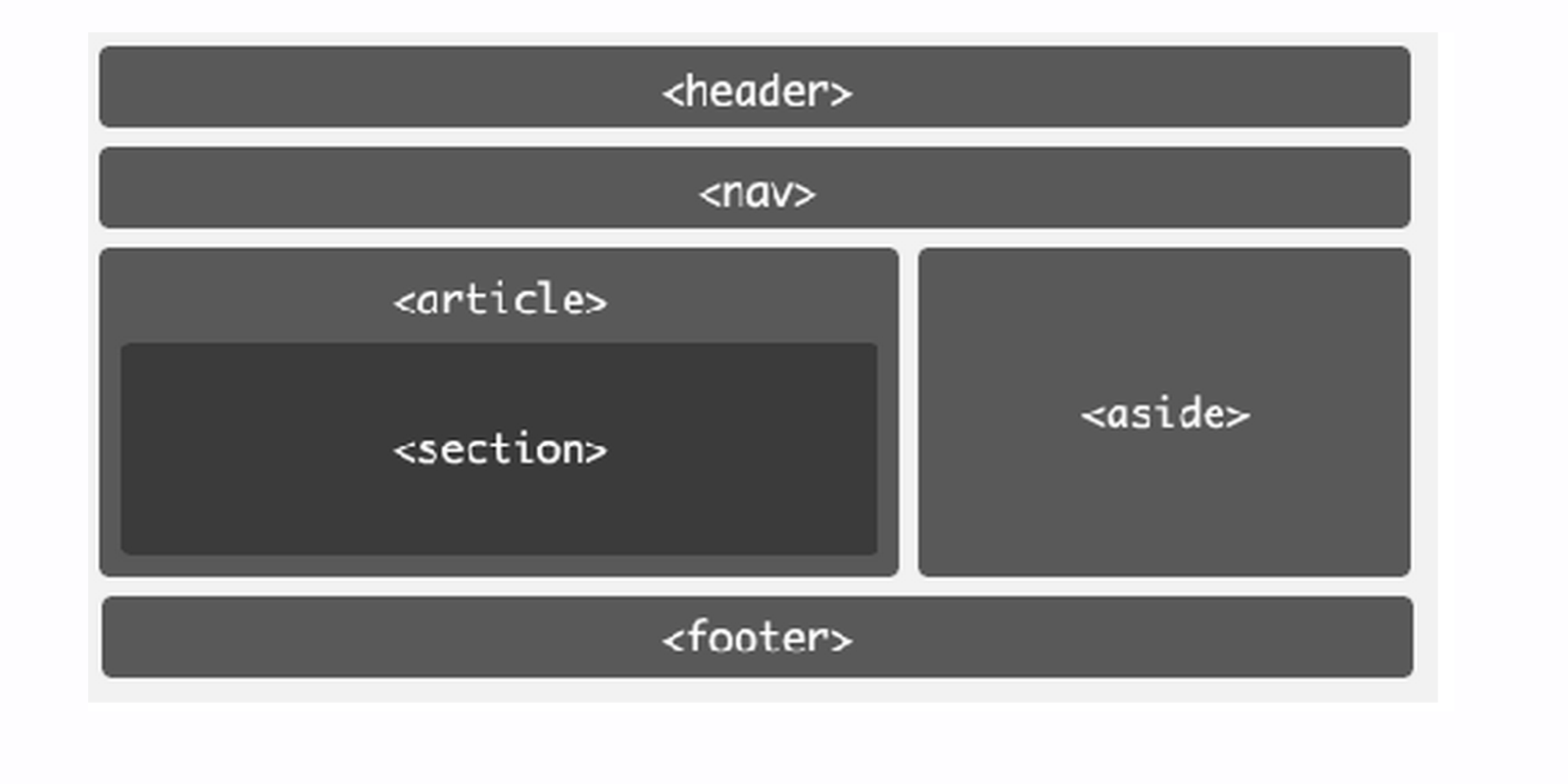
Make sure you distinguish between <head> and <header>, they are not the same